中國哲學書電子化計劃
中國哲學書電子化計劃 (CTP) 是個開源的線上電子圖書館計劃,提供轉錄、閱讀和搜索中國經典和古籍的多項功能。它的宗旨在於提供容易獲取並準確的文本版本[1],尤其和中國哲學相關的文本。這個網站被譽為網絡上最大和準確度最高的中國古典文獻庫,[2][3]也被評為用以研究中國上古文獻的最有用文本庫之一。
這個網站以多種功能的整合,以及API等外部工具為基礎,讓用戶得以對古代文獻進行各種數位分析。藉助CTP API和網站的插件系統,中國哲學書電子化計劃和其他數位計劃是互通的,例如Text Tools、TextRef和MARKUS。
網站內容
這個網站的基本內容包括中國古籍的經過點校和抄本的電子版,也包括基於這些版本而生成的電子文字版。圖版和錄文這兩種內容是互為關聯的。包含這兩種元素的圖文對照界面使得用戶可以在檢閱文字版的同時,參考文字來源的圖錄,並以此有效地進行校對和抄錄工作。圖文對照的界面也允許眾包用戶對文字進行修訂和加上注釋,例如是修正OCR生成的文字版,或對白文加上標點。
Texts are divided into pre-Qin and Han texts, and post-Han texts, with the former categorized by school of thought and the latter by dynasty. The ancient (pre-Qin and Han) section of the database contains over 5 million Chinese characters, the post-Han database over 20 million characters, and the publicly editable wiki section over 5 billion characters.[4] Many texts also have English and Chinese translations, which are paired with the original text paragraph by paragraph as well as phrase by phrase for ease of comparison; this makes it possible for the system to be used as a useful scholarly research tool even by students with little or no knowledge of Chinese.[5] Many works are available in multiple versions, with each transcription following (and often linked to images of) a particular historical edition of the text.
As well as providing customized search functionality suited to Chinese texts,[6][7] the site also attempts to make use of the unique format of the web to offer a range of features relevant to sinologists, including an integrated dictionary, word lists, parallel passage information[8], scanned source texts, concordance and index data,[9] a metadata system, Chinese commentary display,[10] a published resources database, and a discussion forum in which threads can be linked to specific data on the site.[11][12] The "Library" section of the site also includes scanned copies of over 25 million pages of early Chinese texts,[13][14] linked line by line to transcriptions in the full-text database, many creating using Optical Character Recognition,[15] and edited and maintained using an online crowd-sourcing wiki system.[16][17] Textual data and metadata can also be exported using an Application Programming Interface, allowing integration with other online tools as well as use in text mining and digital humanities projects.[16][18]
=功能
A number of functions are integrated directly into the system itself, with many more others accessible through external plugins and APIs. Core functionality includes an integrated dictionary, which summarized available information about words and characters from knowledge encoded throughout the system itself, such as citations from historical dictionaries, phonetic annotations from various historical sources, attested usage of the term, together with translations (where available). The dictionary also allows lookup of non-Unicode characters where these have been attested to in specific locations within the database.
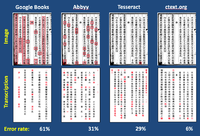
Specially adapted optical character recognition developed for the project and achieving greatly reduced error rates compared with alternative methods is used extensively within the system to provide transcriptions of many texts and editions not previously available in digital form.[19] Transcriptions created through optical character recognition are used to enable full-text search of scanned images of early editions, including those provided by university libraries and other large-scale scanning projects such as the Harvard Yenching Chinese Rare Books Digitization Project. Users of the system collaboratively edit the resulting transcriptions to correct OCR errors as well as add modern punctuation and other annotations to the texts.
As well as providing a mechanism for close integration with external tools and projects, the CTP API and plugin system also provide a powerful means for programmatic access to textual data for use in text mining research and digital humanities teaching. External tools such as Text Tools facilitate browser-based analyses of word usage, text reuse, document similarity, and other aspects of texts contained in the system as well as interactive visualization of results. A Python module interfacing with the same API allows for more specialized data mining research.
參考文獻
- ↑ Elman, Benjamin A. Classical Historiography for Chinese History: Databases & electronic texts. Princeton University. [June 3, 2016].
- ↑ Association of Chinese Philosophers in North America (北美中國哲學學者協會)
- ↑ Chris Fraser, Department of Philosophy, University of Hong Kong
- ↑ http://ctext.org/system-statistics
- ↑ Connolly, Tim. Learning Chinese Philosophy with Commentaries. Teaching Philosophy (Philosophy Documentation Center). 2012, 35 (1): 1–18 [March 19, 2017].
- ↑ http://ctext.org/instructions/advanced-search
- ↑ http://ctext.org/faq/normalization
- ↑ Sturgeon, Donald. Unsupervised identification of text reuse in early Chinese literature. Digital Scholarship in the Humanities (Oxford University Press). 2017 [November 21, 2017].
- ↑ Xu, Jiajin. Corpus-based Chinese studies: A historical review from the 1920s to the present. Chinese Language & Discourse (John Benjamins Publishing Company). 2015, 6 (2): 218–244 [June 3, 2016].
- ↑ Adkins, Martha A. Web Review: Online Resources for the Study of Chinese Religion and Philosophy. Theological Librarianship (American Theological Library Association). 2016, 9 (2): 5–8 [November 7, 2016].
- ↑ Holger Schneider and Jeff Tharsen, http://dissertationreviews.org/archives/9213
- ↑ http://ctext.org/introduction
- ↑ http://ctext.org/library.pl?if=en
- ↑ http://ctext.org/system-statistics
- ↑ Template:Cite conference
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 https://cpianalysis.org/2016/06/08/crowdsourcing-apis-and-a-digital-library-of-chinese/, China Policy Institute, University of Nottingham
- ↑ http://ctext.org/instructions/ocr
- ↑ http://ctext.org/tools/api
- ↑ Template:Cite conference