China Historical Geographic Information System
The China Historical Geographic Information System (CHGIS) is a historical GIS project that has created spatial datasets of populated places and historical administrative units for the period of China's history between 221 BCE and 1911 CE. CHGIS tracks changes in place names, administrative status, and geography. It is a joint project of the Fairbank Center for Chinese Studies at Harvard University and the Center for Historical Geography at Fudan University. General Editors: Professors Peter K. Bol of Harvard.[1] and Ge Jianxiong of Fudan University. Executive editors: Merrick Lex Berman of Harvard University and Man Zhimin of Fudan Univeristy. [2]. For complete information see the CHGIS homepage.
Contents
Online Gazetteer and API
CHGIS data can be searched online through its Temporal Gazetteer.
TGAZ API - is a read-only interface designed to search the contents of the China Historical GIS placename database. The TGAZ system architecture -- based loosely on the CHGIS XML API (2006) -- has been normalized and made more generic in order to integrate multiple data sources, and to allow for vernacular spellings or transcription methods in many languages.
This interface accepts queries for placenames in UTF-8 encoded strings or glyphs (for example, Chinese Simplified or Complex characters). Each placename recorded in the database is referred to as a spelling. A brief look at the project in diagrams (PDF). See the demonstration on YouTube
Purpose and Scope
The main objective of the CHGIS project is to create a flexible tool, in the form of a documented database of places and administrative units, which can be used to investigate any sort of geographically specific data related to China's imperial history. The unique ID numbers for each of the CHGIS temporal instance records can be used as geocodes in relational databases, or to mark up texts, enabling users to import their own datasets into the CHGIS platform. Users will be able to associate their own data with CHGIS records, and then use the CHGIS database to sort, query, and display their data for different historical periods and at different levels of aggregation.
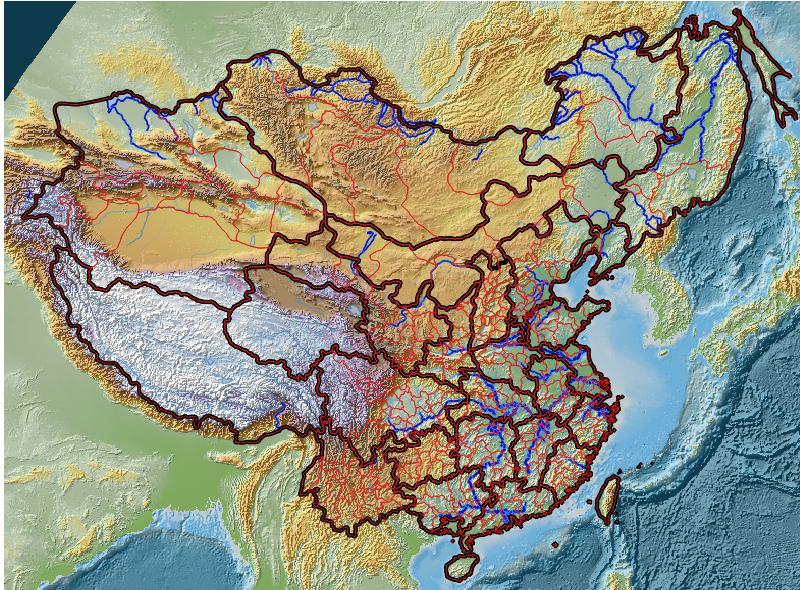
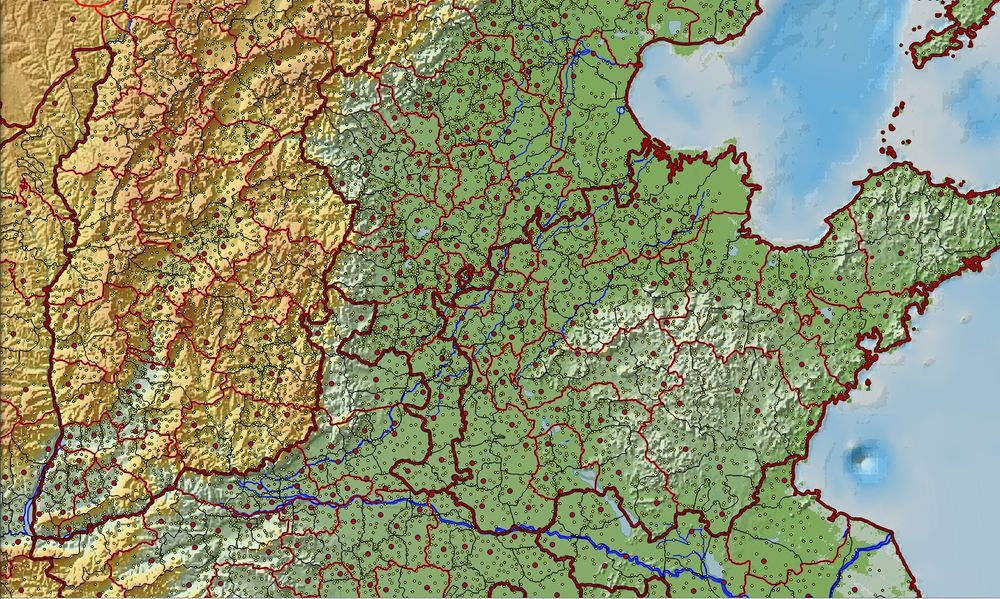
The CHGIS project has been working backwards from county basemaps for the year 1911, to create a continuous time series of records that track changes in placename, administrative status, and geographic locations. It should be noted that the data for the year 1911 CE is time slice valid for a single year, and the content overlaps the time series data.
There have been six versions of CHGIS data released between (2002 - 2016), providing base coverage of the so-called core provinces of Dynastic China: Anhui, Fujian, Gansu, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hebei, Henan, Heilongjiang, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Liaoning, Ningxia, Shandong, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang.
The following provinces lie outside the scope of the current project for Time Series data: Neimeng, Qinghai, Xinjiang, and Xizang. However they do exist in the two Time Slice datasets for 1820 and 1911.
Available Datasets
CHGIS Version 6 Datasets include the following layers.
Time Series
All are available in GBK and UTF8 encoding.
NOTE: prefectural level polygons are complete only for the period 1350-1911.
Time Slice 1820
The 1820 Time Slice includes: county, prefectural and provincial level points (administrative seats), township points, prefectural level and provincial level polygons, rivers and lakes.
Time Slice 1911
The 1911 Time Slice includes: county, prefectural and provincial level points (administrative seats), township points, county, prefectural and provincial level polygons.
Time Slice 1990
CHGIS also distributes the CITAS dataset of county, prefectural and provincial polygons as of 1990.
Digital Elevation Model
The basemap image for Digital Elevation was created from GTOP0-30 Nasa dataset, with approximately 1km resolution per pixel. There are two versions available, one for ESRI, one for QGIS, both of which are based on the files: chgis_dem.tif and chgis_hillshade.tif.
Coastline (circa 1820)
The coastline is a vector polyline useful for showing the mouth of the Yellow River to the South of the Shandong Peninsula (near Lianyungang). After the floods of 1850s and 1897, the Yellow River remained in its present course, emptying North of the Shandong peninsula, into the Bohai sea.
Rivers (circa 1820)
The Coded Rivers dataset contains polylines of the the major and minor rivers, with Chinese names for the major rivers. The Strahler Order of the rivers is provided, so that they can be symbolized with graduated sizes, showing the generalized view of minor rivers draining into the major rivers and to the sea.
Coverages
See also
- China Biographical Database (CBDB)
References
- ↑ "PETER K. BOL". Harvard University. Retrieved 17 November 2017.
- ↑ Peter Bol; Jianxiong Ge (2005). "China Historical GIS". Historical Geography.